Internal Friction of Materials
The solution of a set of problems associated with the nature, measurements, evaluation and application of information on the internal friction and the defect of the Young modulus of materials is based on a brief and functional characterisation of the elasticity parameters of structural monoliths and composite materials, and also on the evaluation of the effect of different internal and external factors on their magnitude. A special position is occupied by the effect of factors causing nonlinearity between stress and strain, i.e. anelastic behaviour of the materials. This includes the explanation of the phenomenon of deformation lagging behind stress, irreversible scattering of energy in materials and mechanisms by which the energy of vibrations is irreversibly scattered in the materials. These processes are also reflected in the level of the Young modulus and the occurrence of defects of the Young modulus, and this may influence the accuracy of calculations of permitted stresses in components or whole structures.
Under the effect of a generally oriented force the solid can change its dimensions and shape. If the relative strain in a specific direction is denoted by the strain sensor mn and the force per unit cross-section, causing this strain, is denoted as the stress sensor ik, then
| (2.1) | 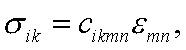 |
| (2.2) |  |
where c ikmn and s nmik are the elasticity constants. Strain tensor ? mn and stress tensor ? ik are the tensors of the second order. They can be described by nine pairs of strain components...
