Water and Wastewater Calculations Manual

The weight ( W) of an object, in the International System of Units (SI), is defined as the product of its mass ( m, in grams, kilograms, etc.) and the gravitational acceleration ( g = 9.81 m/s 2 on the earth's surface) by Newton's second law of motion: F = ma. The weight is expressed as
The unit of weight is kg m/s 2 and is usually expressed as newton (N).
In the SI system, one newton is defined as the force needed to accelerate 1 kg of mass at a rate of 1 m/s 2. Therefore
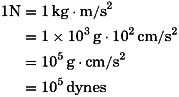
In the British system, mass is expressed in slugs. One slug is defined as the mass of an object which needs one pound of force to accelerate to one ft/s 2, i.e.
What is the value of the gravitational acceleration ( g) in the British system?
solution:
| Note | This is commonly used as g = 32.2 ft/s 2. |
The specific weight (weight per unit volume) of a fluid such as water, ?, is defined by the product of the density ( ?) and the gravitational acceleration ( g), i.e.
Water at 4 C reaches its maximum density of 1000 kg/m 3 or 1.000 g/cm 3. The ratio of the specific weight of any liquid to that of water at 4 C is called the specific gravity...
