Bistatic Radar, 2nd Edition

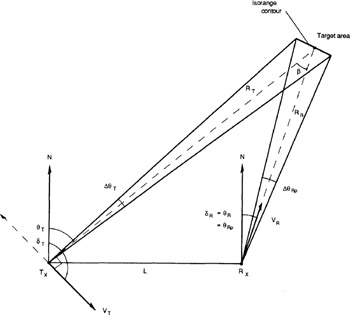
When both the bistatic transmitter and receiver are moving, for example, airborne or spaceborne, they generate a clutter doppler shift, (6.5), and a clutter doppler spread, (6.11). Because both platforms contribute to the shift and spread, this type of bistatic radar has an additional degree of freedom in Controlling doppler from ground clutter by changing velocity vectors ( V T, ? T, and V R, ? R) or geometry ( ? T, ? R, R T, R R, and L). This concept is called clutter tuning, and applies to both SAR and MTI operation.
The principal application of clutter tuning is forward-looking SAR. The transmitter flies with its velocity vector perpendicular to its look angle, and the receiver flies with its velocity vector colinear with its look angle, i.e., directly at the target area, as shown in Figure 12.14. In this case, ? T = ? T 90 and ? R = ? R. Thus, the bistatic SAR isorange resolution, ? i is from (7.17):
where T is the array time.
Equation (12.26) shows that the resolution is independent of receiver range and velocity. Also the resolution is degraded (increased) by a factor 2/cos( ?/2) when compared to the cross-range resolution obtained if the transmitter were operating as a monostatic radar, (7.10).
The operational utility of forward-looking SAR is...
