Applied Electromagnetics Using Quickfield & MATLAB

The basic equation of steady state current flow is ? J = 0 or ? ( E/ ?) = 0, where E = - ? U so that
| (9.1) | |
where ? is resistivity with units of ? m. Note that ? = 1/ ?, where ? is the electrical conductivity in S/m. Once U is determined, the current density may be calculated from Ohm's law J = ? E or
| (9.2) | |
From equation (9.1) the scalar potential will satisfy Laplace's equation ? 2 U = 0 in regions of constant resistivity.
In Cartesian coordinates, equation (9.1) for steady state current flow is
| (9.3) | 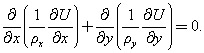 |
In axial symmetric cylindrical coordinates
| (9.4) |  |
The electric field may be calculated from the gradient of the scalar potential as in Chapter 4. The total energy may be calculated from the electrical current density
| (9.5) | |
Assign specific electric potential U values on exterior boundaries or edges within the solution region. This condition must be applied to at least one point in the solution region. Position dependent Dirichlet conditions may be entered using the formula editor.
Specify the normal DC current density on either exterior boundaries as ![]() or interior boundaries as ? J n = ( J + - J -)
or interior boundaries as ? J n = ( J + - J -) ![]() The Neumann condition
The Neumann condition
