Fundamentals of Signals and Systems

The Laplace transform is a very useful tool for analyzing linear time-invariant (LTI) electric circuits. It can be used to solve the differential equation relating an input voltage or current signal to another output signal in the circuit. It can also be used to analyze the circuit directly in the Laplace domain, where circuit components are replaced by their impedances seen as transfer functions.
Let us quickly review some of the fundamentals of circuit analysis, such as nodal and mesh analysis based on Kirchhoff' s current and voltage laws.
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) states that the sum of all currents entering a node is equal to zero. This law can be used to analyze a circuit by writing the current equations at the nodes (nodal analysis) and solving for the node voltages. Nodal analysis is usually applied when the unknowns are voltages. For a circuit with N nodes and N - 1 unknown node voltages, one needs to solve N - 1 nodal equations.
Suppose we have the resistor-inductor-capacitor ( RLC) circuit of Figure 9.1 and we want to solve for the voltage across the resistor v( t).
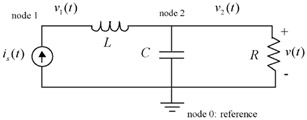
There are three nodes. The bottom one is taken to be the reference node (voltage = 0). We can solve this circuit...
